Gait analysis is the systematic study of human motion, using the eye and the brain of observers, augmented by instrumentation for measuring body movements, body mechanics, and the activity of the muscles. It is used to assess, plan, and treat individuals with conditions affecting their ability to walk.
Here's a high-level overview of gait analysis in the context of chiropractic care:
Purpose: Gait analysis is used in chiropractic to identify abnormalities in the locomotor system that could be causing or contributing to pain or discomfort. It can help diagnose conditions related to poor biomechanics, such as repetitive strain injuries, back pain, or conditions caused by imbalances in the musculoskeletal system.
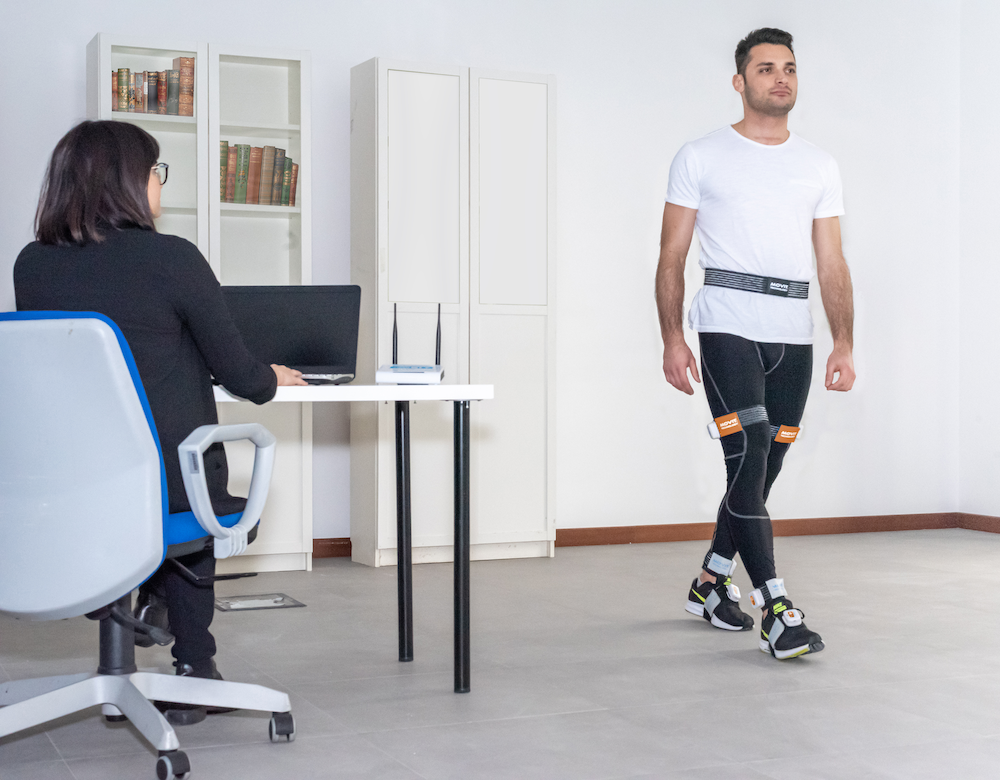
Observational Analysis: The most basic form of gait analysis is observational, which involves the chiropractor watching a patient walk and noting any deviations from what is considered normal gait. This can include limping, uneven stride length, excessive arm swing, foot dragging, and more.
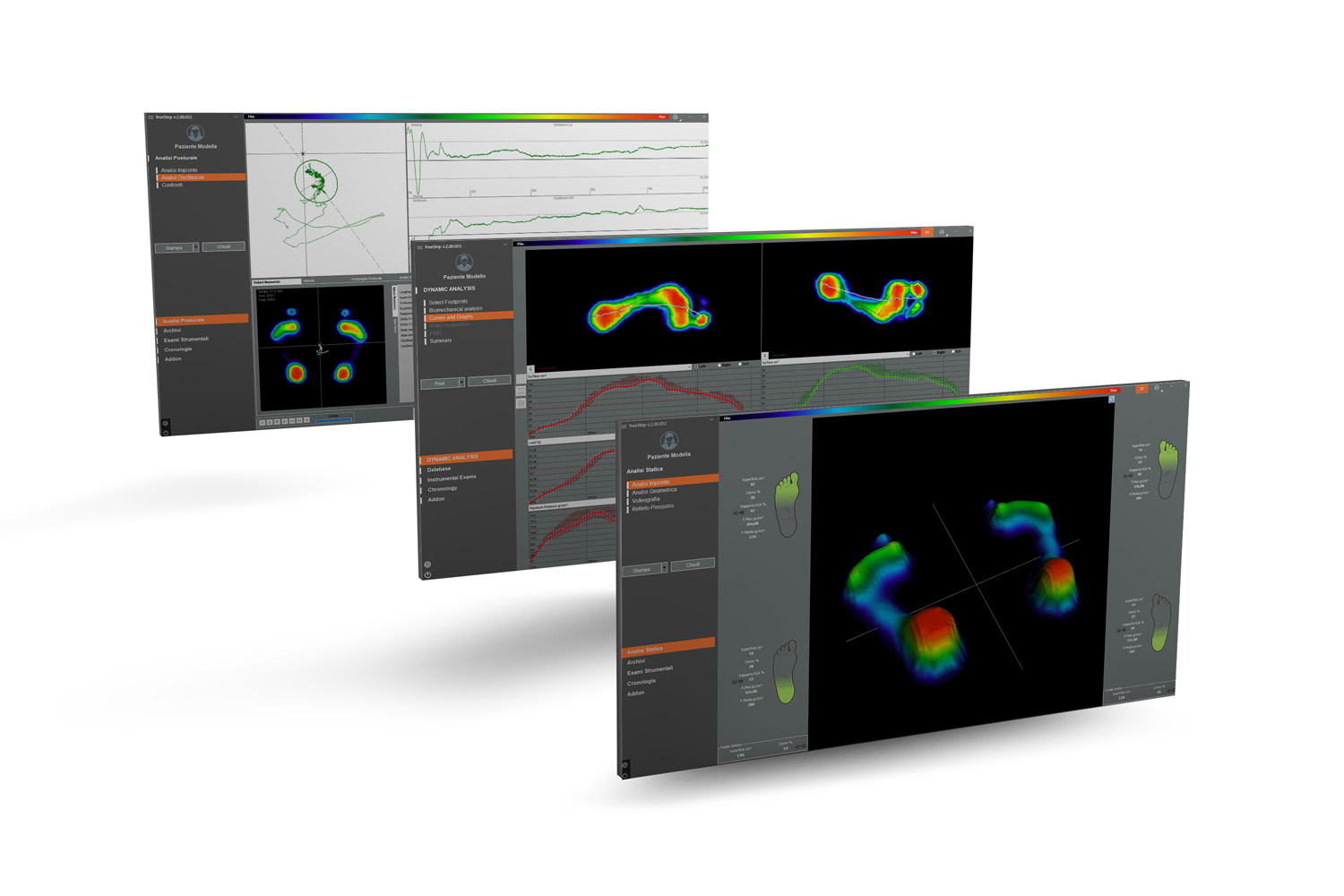
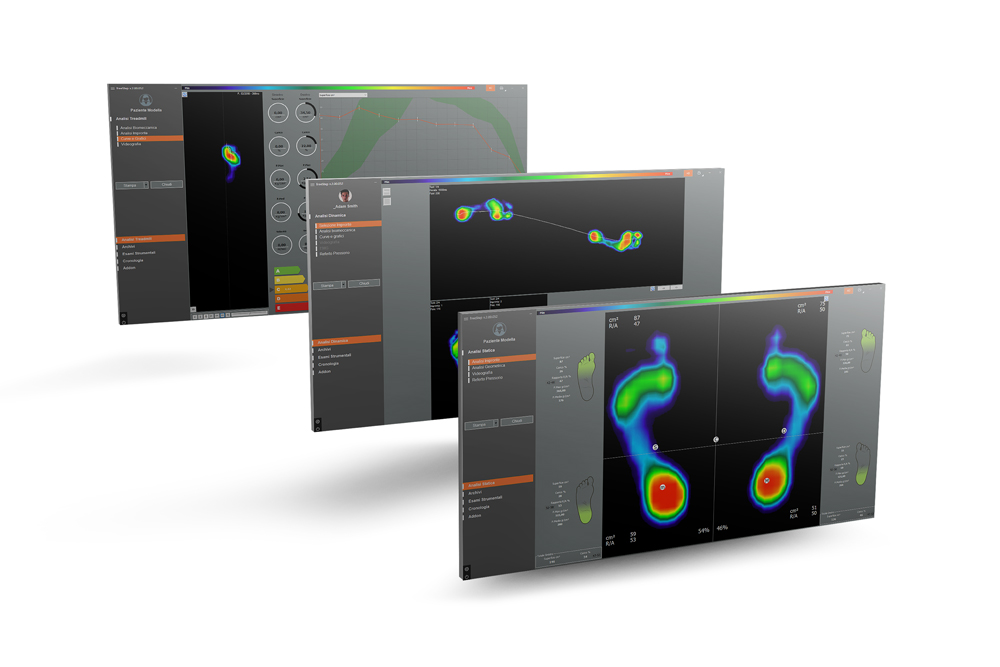
Instrumented Analysis: In some cases, a more in-depth gait analysis may be necessary. This can involve the use of specialized equipment like force plates (such as the
Sensor Medica Freemed Platform), motion capture systems(Like the
Moover Gait system), electromyography (EMG) for muscle activity, and more. These tools provide a more objective and precise measurement of gait parameters.
Phases of Gait: Understanding the phases of gait - heel strike, mid-stance, push-off (toe-off), and swing phase - is critical. Each phase can be associated with specific biomechanical actions in different body parts, and problems in one phase can affect the entire gait cycle.
Biomechanics: Gait analysis involves understanding the biomechanics of the human body. This includes the study of the movements of the skeletal system and the forces that act upon it. Chiropractors must understand how different parts of the body interact during movement to identify and treat gait-related issues.
Treatment: Once problems have been identified through gait analysis, chiropractors can use a range of treatments to address them. This could include spinal adjustments, massage, physical therapy exercises, and advice on proper footwear or orthotics. The goal is to correct the identified gait abnormalities, reduce pain, and improve mobility.
What form can a gait and biomechanics assessment take - what's an example of a workflow to integrate into your clinic when considering gait?Importance of the Initial Visit: When a new patient comes to a chiropractic clinic, assessing foot function and gait analysis can provide critical insights. Many patients may have been to various healthcare practitioners without finding relief for their ailments. The chiropractor can impress upon these patients their thoroughness and skill by including foot function and gait analysis in their initial assessment.
Root Cause Analysis: Patients often consult specialists who tend to focus on symptoms, treating pain with medication, injections, or surgery, rather than addressing the root cause. In many cases, the root cause could be dysfunctional feet. A thorough chiropractic examination can help identify such root causes and potentially provide more effective treatment.
Feet as the Body's Foundation: Feet serve as the body's foundation and provide critical information about the stability and biomechanical state of a person's entire body. Patients often don't realize that the foot has three arches rather than just one. Understanding the "foot-spine connection" can be a powerful tool in helping a patient comprehend how stresses affect the body from the feet up to the head and jaw.
Examination of Feet: When examining the feet, the chiropractor will observe the state of the three arches. Most patients exhibit excessive foot pronation, which puts stress on various parts of the body, including ankles, knees, hips, spine, shoulders, and jaw. There are several visual changes and "red flags" that can indicate overpronation, such as bunions, hammer toes, calluses, foot flare, internal knee rotation, and more.
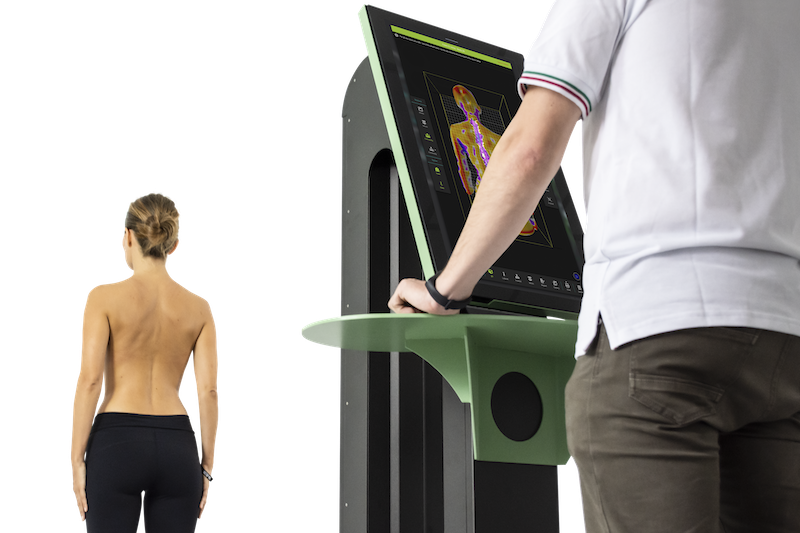
Digital Foot Scanner: A weight-bearing,
3D, laser digital foot scanner can provide accurate assessments of the state of the arches underneath the feet, indicating the severity of any arch collapse.
Gait Analysis: The gait cycle has two phases, the Swing Phase and the Stance Phase, with the latter being more clinically relevant. The Stance Phase consists of three parts: Heel Strike, Foot Flat, and Toe Off. During the Foot Flat portion, the tibia and femur bones internally rotate.
In cases of overpronation, these bones excessively internally rotate with every step, which can stress various joints and lead to wear and tear on cartilage and connective tissues, thus increasing the risk of arthritis, soft tissue injuries, and pain.
The Role of Orthotics: The evaluation of feet can reveal the critical role they play in overall body stability and stress. If the arches are flat, the feet cannot absorb shock and distribute forces safely for the body. Custom-molded, three-arch orthotics can be recommended to not only support the patient's feet but also stabilise the whole body from the ground up.
So there you have it, a quick overview of the role of gait analysis in Chiropractic. It's not just about custom orthotics, although if you are looking to boost clinic revenues that's a great route to take!
Gait can signpost lower limb issues that will roll into spinal challenges for your patients. Understanding how to diagnose them, and having the correct equipment to diagnose and educate your patients is the way of the modern, forward-thinking chiropractic clinic.
If you have more questions, hit the WhatsApp button to the right and start up a conversation!