Understanding the Concept of Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is a powerful tool that helps us understand how we walk and run. It is the study of human motion, using the eye and the brain of observers, augmented by instrumentation for measuring body movements, body mechanics, and the activity of the muscles. In simple terms, it's like a detailed sports replay, breaking down the action into specific phases to see what's really going on. In the context of diagnosing biomechanical issues, gait analysis can provide critical insights.
It can highlight abnormalities in our movement pattern, which might be causing problems like recurring injuries or decreased performance. So, understanding gait analysis is a key step in identifying and fixing these issues.

The Science Behind Gait Analysis: A Closer Look
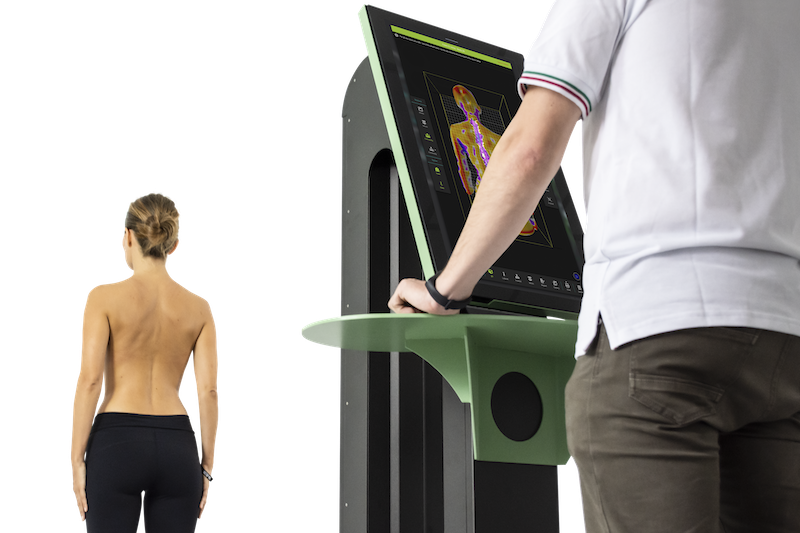
Gait analysis is a powerful tool in diagnosing biomechanical issues, and the science behind it is fascinating. It involves studying the way you walk or run, using advanced technology to capture data about your body's movements. This data is then analysed to reveal any abnormalities in your gait that could indicate underlying health problems. It's a highly precise method, able to spot even slight deviations from a normal gait. The beauty of gait analysis is that it's non-invasive and can provide valuable insights into your overall health and wellbeing. It's a tool that has transformed the way we diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions, from joint issues to neurological disorders.
The Role of Gait Analysis in Diagnosing Biomechanical Issues
Gait analysis plays a crucial role in diagnosing biomechanical issues. It's a method used to assess the way we walk or run, highlighting any abnormalities in our movements. Medical professionals use this technique to spot any problems early, often before they start causing pain or discomfort. By studying the movement and coordination of our muscles and joints, they can identify inconsistencies that might lead to injuries or conditions such as arthritis. So, gait analysis is a powerful tool, giving experts the ability to diagnose issues and plan effective treatment strategies, ultimately helping us maintain our mobility and quality of life.
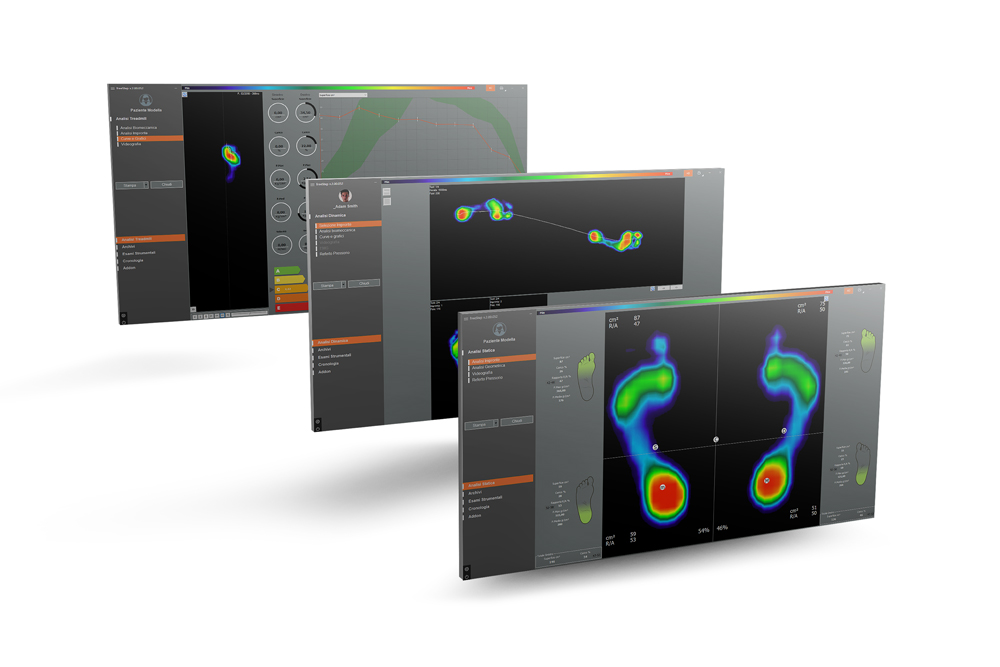
Common Biomechanical Issues Detected Through Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is a powerful tool for diagnosing common biomechanical issues. These include overpronation, where the foot rolls inward excessively during walking or running, and supination, where the foot rolls outward. Both can lead to injury if not addressed. Gait analysis can also identify uneven weight distribution, which could indicate a limb length discrepancy or hip alignment issue. Additionally, it can detect abnormal patterns in foot lift and strike, which may suggest muscle weakness or nerve damage. By analysing these aspects of a person's walk, healthcare professionals can devise effective treatment plans to correct these issues and prevent further complications.
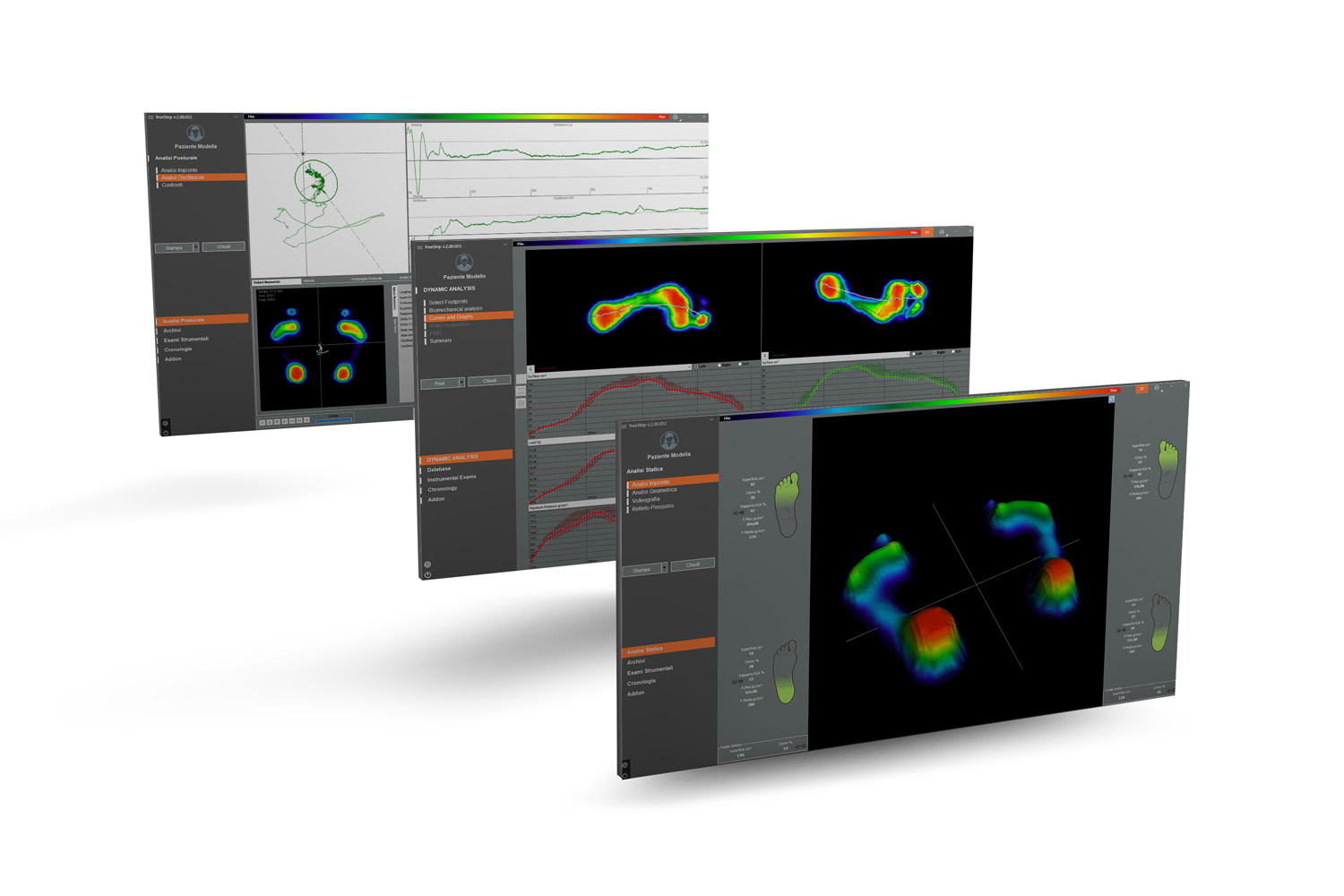
The Process of Gait Analysis: A Step-by-step Guide
Gait analysis is a powerful tool in diagnosing biomechanical issues in the body, which may affect your mobility. The process begins by observing your regular walking pattern. A trained professional will watch you walk, noting the movement and coordination of your limbs. Next, you may walk or run on a treadmill connected to a computer. This machine records data about your stride, speed, and impact force. Using this data, the professional can identify any irregularities in your gait that could be causing discomfort or injury. Through this step-by-step process, gait analysis can help pinpoint the root cause of your mobility issues, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
Advancements in Gait Analysis Technology: Impact on Diagnosis Accuracy
Gait analysis technology has seen significant advancements in recent years, and it's having a profound impact on the accuracy of diagnosing biomechanical issues. This technology uses sensors and cameras to capture detailed information about a person's walking pattern. It provides an in-depth look at how the muscles, joints, and limbs interact during movement. These advancements have made it possible to detect subtle abnormalities that might be overlooked in a traditional physical examination. This means doctors can now diagnose conditions more accurately, leading to more effective treatment plans. The power of gait analysis lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of a person's biomechanics, significantly improving patient care.
The Future of Gait Analysis: Predictions and Possibilities
The future of gait analysis holds immense potential in diagnosing and treating biomechanical issues. With advancements in technology, we predict a more accurate and detailed analysis of a person's gait. This means health professionals will have a better understanding of your walking pattern and can pinpoint any abnormalities more precisely. This could lead to early detection and treatment of various physical conditions. In the future, gait analysis might even be used for predicting potential injuries before they occur, opening up exciting possibilities for preventative healthcare.
Conclusion: The Undeniable Importance of Gait Analysis in Biomechanics.
In conclusion, the significance of gait analysis in biomechanics cannot be overstated. It is a powerful tool that provides valuable insights into diagnosing and treating a range of biomechanical issues. By examining the way a person walks or runs, healthcare professionals can identify abnormalities, measure body movement, understand muscle activity, and ultimately, devise effective treatment plans. So, whether it's improving athletic performance or rehabilitating a patient after surgery, gait analysis plays a crucial role. It's a game-changer, making it easier to enhance mobility and improve quality of life.